Innovation Drove Capital Region Export Growth
In 2017, exports from the Capital Region increased over the year by 2.6 percent, with its R&D to Commercialization Cluster driving most of that gain, according to a Center for Economic Growth (CEG) analysis of data from the Brookings Institution’s 2018 Export Monitor.
Innovation-Related Exports
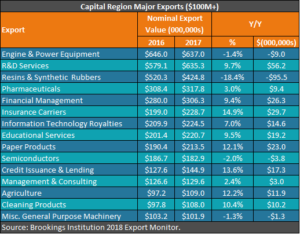
In 2017, nominal (current dollar) exports from the eight-county Capital Region totaled $6.03 billion, up $153.3 million from the previous year. Much of that growth was attributable the region’s R&D services and tech-related royalties from the use of U.S. patents, trademarks and copyrights.
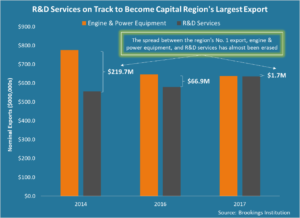
Over the year, R&D services exports increased by 9.7 percent to $635.3 million. That made R&D services the region’s second largest export by dollar value, trailing engine and power equipment. Whereas the spread between the two was $219.7 million in 2014 and $66.9 million in 2016, it had narrowed to $1.7 million last year. At this rate, R&D services are on track to become the Capital Region’s largest export by dollar value.
In 2017, R&D services exports directly supported 888 jobs in the Capital Region, up 7.4 percent from the previous year. The total jobs impact for R&D services exports in 2017 was 4,163, up 18.3 percent from 2016. According to Brookings, direct export production jobs are “jobs supported by exports in the industries producing the exported good or service,” and total export-supported jobs are “jobs with the suppliers of intermediate inputs to exporting industries.”
With a 92.1 percent year-over-year increase to $65 million, other manufacturing royalties1 were the region’s fastest-growing export. Other fast-growing, innovation-related exports were information technology royalties2 (up 7 percent to $224.5 million) and scientific and technical royalties3 (up 10.7 percent to $29.3 million). However, other computer and electronic royalties and chemical manufacturing royalties declined by 4.7 percent and 7 percent, respectively.
R&D to Commercialization Cluster
In 2015, the Capital Region Economic Development Council (CREDC) developed a regional economic cluster plan for the R&D to Commercialization Cluster. This cluster employed 21,930 in 2017, and REDC plans to grow it by pursuing the following strategies, as detailed in the Council’s 2017 Progress Report:
• Harness the innovative power of the region’s university and private research centers to drive economic multiplier effects and support many high- and medium-skilled jobs.
• Expand and fortify the region’s network of university incubators and accelerators, including those associated with Innovate 518 (see page 34) to assist startups with technology transfer.
• Assist entrepreneurs and innovators in developing prototypes and building their businesses through the establishment of maker spaces and co-working spaces.
• Leverage CEG’s expertise and status as the region’s designated Regional Technology Development Center to improve the efficiency of technology startups and manufacturers.
In addition to housing major academic R&D operations at SUNY Polytechnic Institute, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Albany Medical College, the University at Albany and Union College, the Capital Region includes the following industry R&D powerhouses:
- AMRI
- Angiodynamics,
- GE Global Research
- GlobalFoundries
- Momentive Performance Materials
- Regeneron
- Sabic
- SI Group
Manufacturing Export’s
Among the Capital Region’s major exported manufactured goods ($100 million or more) were paper products and pharmaceuticals, up 12.1 and 3 percent, respectively. Semiconductor and miscellaneous general purpose machinery exports were down 2 percent and 1.3 percent, respectively.
CEG Activities to Support Trade
CEG is working to further grow the Capital Region’s exports through the following activities:
• Promoting the Capital Region’s R&D assets and opportunities at international conferences, such as Silicon Europa in Munich, Germany, the Select USA Canadian International Auto Show in Ontario, Canada, and Bio International in Boston
• Helping manufacturers develop proactive and strategic approaches to international markets through the Exportech program.
• Representing Albany seaports at the International Offshore Wind Partnering Forum in Princeton and working to position them to become staging, fabrication, logistics sites for the offshore (OSW) wind industry
Notes
- 1 Includes NAICS 311; 312; 313; 314; 315; 316; 321; 322; 323; 324;
- 326 327; 331; 332; 333; 335; 336; 337; 339
- 2 Includes NAICS 522; 523; 524; 525; 531; 532; 533; 541; 551; 561; 562
- 3 Includes NAICS 511; 517; 519
Don’t miss these insights into the trends that are shaping the Capital Region’s economy. Sign up for CEG’s e-news and follow us on: